Customer service representatives (CSRs) are pivotal in shaping customer experiences and building brand loyalty. They handle everything from answering questions to resolving complaints, giving you loyal, satisfied customers.
But hiring and retaining top-tier CSRs can be tough. You often face a tightrope act: balancing competitive compensation with budget constraints and evolving market demands.
Don’t worry. To help you out, we’ve put together a comprehensive guide on what to pay customer service representatives. Let’s get into it!
How we researched this topic
To ensure the information in this article is accurate and reliable, we’ve used data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), specifically the latest Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics (OEWS) report for CSRs.
The BLS, a trusted government resource, gathered primary report data by surveying around 1.1 million organizations in the US from November 2020 to May 2023. We’ve compiled the most relevant data to help give you an accurate lowdown on what CSRs typically earn so you can make more informed decisions about compensating them.
Key takeaways
The median annual salary for customer service representatives in the US is $39,680, with hourly wages averaging $19.08.
Location significantly impacts pay: Metropolitan areas typically offer higher wages than rural regions.
The oil and gas and industrial manufacturing industries pay CSRs more than the restaurant and recreation industries.
Compensation packages with benefits like health insurance, paid time off (PTO), and professional development opportunities are essential for attracting and retaining CSR talent.
The best insights on HR and recruitment, delivered to your inbox.
Biweekly updates. No spam. Unsubscribe any time.
National salary statistics for CSRs
Pay metric | Annual wage (USD) | Hourly wage (USD) |
Median | $39,680 | $19.08 |
Mean | $43,520 | $20.92 |
Top 10% earners | $61,250 | $29.45 |
Bottom 10% earners | $29,560 | $14.21 |
Median salary vs. mean salary
Here’s the difference between the median and mean values:
The median is the halfway point between the highest and lowest salary figures. Half of CSRs earn more than the median, and half earn less. The median is a more accurate way of determining a typical salary because extreme salaries don’t affect it.
The mean is the average of all salaries divided by the number of people in the profession. It helps us understand overall trends, but because the mean accounts for all earnings, it can be skewed by extreme values.
Why does the difference matter? Most CSRs earn just below $40,000, but some CSRs in higher-paying industries may earn more than $90,000. These higher salaries can pull the mean up by a few thousand, making it seem like most CSRs earn more than they do. However, the median remains at $40,000, offering a more accurate picture of what most CSRs make.
Factors influencing salaries
While nationwide statistics can give you an idea of CSR salaries, you should understand how wages differ at various levels to compensate appropriately for open CSR positions.
Consider the following factors that influence customer service representative salaries:
Geographic location: The cost of living and demand for CSRs affect pay across different states. For example, CSRs based in New York City might earn more than those in Houston, TX, because living in New York is more expensive. Similarly, a high demand for CSRs in tech and business hubs such as San Francisco can lead to better salaries than those offered in smaller cities and towns.
Industry-specific factors: The unique challenges in different sectors can impact CSR salaries. For instance, CSRs working in oil and gas and aerospace parts manufacturing industries can earn more than those working in restaurants and sports centers.
Experience level: Veteran CSRs who can strategize, manage large teams, and deal with complex tasks have more earning potential than more junior CSRs.
Education and certifications: Typically, more pay comes with more credentials and professional qualifications. For example, a customer service representative with an International Customer Service Association (ICSA) CSR certification might earn more than a non-certified CSR.
Role responsibilities and required skills: The job scope and skills required of a CSR directly impact pay. A CSR working at a florist or gas station, for instance, will likely earn less than someone assisting ultra-high-net-worth clients with cross-border transactions.
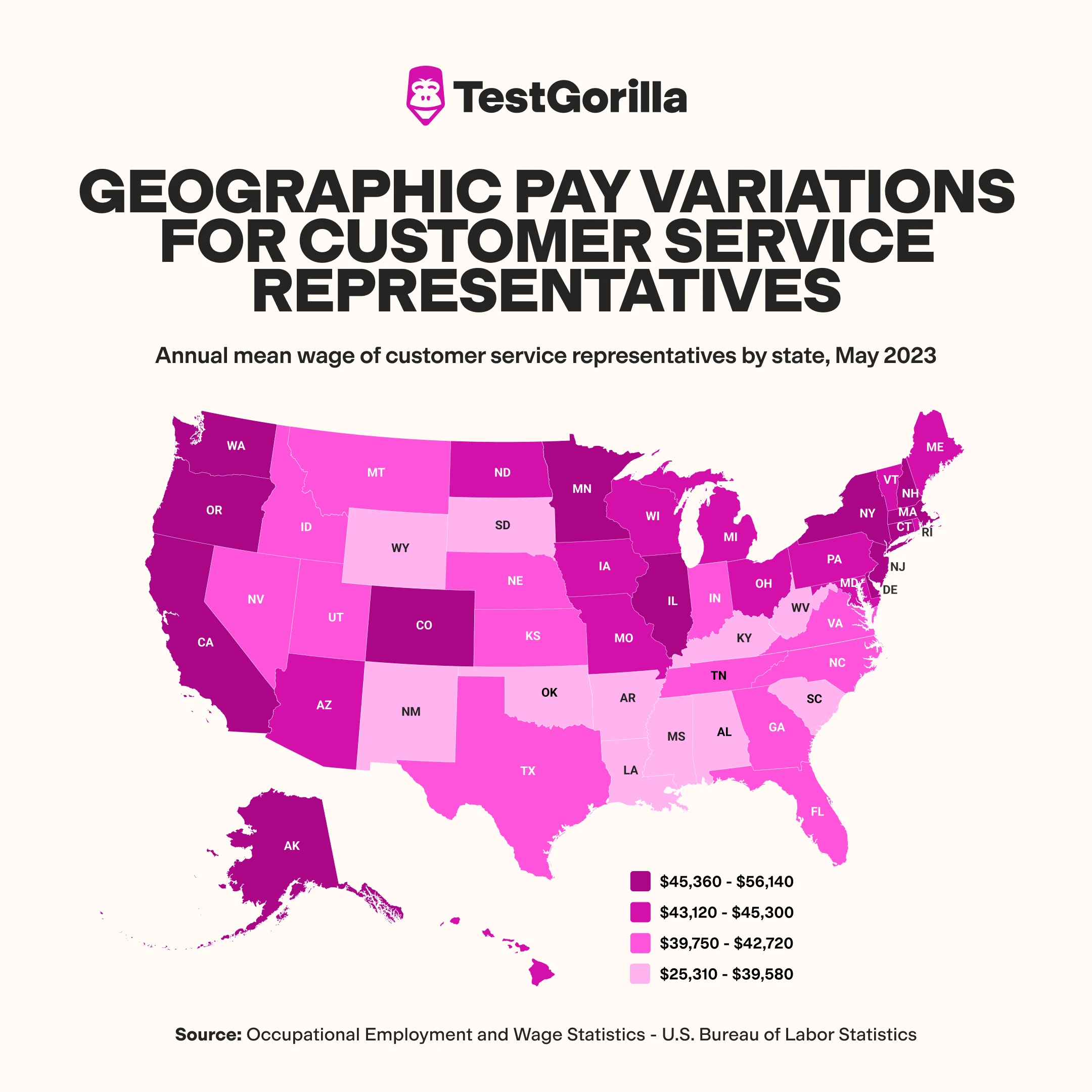
Geographic pay variations
Let’s take a closer look at how customer service representative salaries vary by location.
5 highest-paying states
The BLS notes that these five areas pay CSRs the most – an average of $46,140 to $50,820 a year:
District of Columbia (DC)
Washington (WA)
Massachusetts (MA)
Minnesota (MN)
New York (NY)
5 lowest-paying states
At the same time, these states pay CSRs the least – an average of $33,700 to $36,170 per year:
Mississippi (MS)
Louisiana (LA)
Arkansas (AR)
West Virginia (WV)
Alabama (AL)
There are two big reasons for this difference in pay.
One is the varying cost of living. Forbes found that the average monthly rent in DC is $1,901, but less than half this – $992 – in WV.
The other is the reason for the demand for CSRs in different states. In fact, the data does not suggest that there’s a higher demand for CSRs in higher-paying states. Allows us to explain.
While not the highest-paying states, CSRs in Utah, Arizona, and Georgia account for up to a third of employment in each of those states – with the BLS highlighting an annual mean wage of around $40,000. Why? Because lower-paying states often see higher employment due to industry-specific needs or a larger service-based economy.
Conversely, in high-paying states, wages reflect the cost of living and skill specialization rather than raw demand (as in lower-paying states). High-paying states often have industries with complex customer service needs (in industries like finance and technology). Roles in these industries may require specialized skills, justifying higher pay – but not necessarily creating more positions.
Here are the main reasons you might consider offering lower salaries while still targeting skilled workers:
Cost efficiency: You can strategically locate customer service operations in regions with lower labor costs to maximize your profit margins – especially if you’re focused on outsourcing or are in a call-center-based industry, where the primary goal is cost reduction.
Abundant entry-level talent: Lower-cost areas often have larger pools of candidates willing to work in entry-level positions. Opportunities in higher-paying industries like tech or finance are much rarer, making customer service a major employment avenue for most people.
Lower overheads: Beyond salaries, operating costs like office space, utilities, and infrastructure are also cheaper in low-cost regions – ideal if you’re setting up customer service centers. Better yet: Leverage remote work trends and hire top CSRs living in states with low costs of living to serve your global customer base.
Industry-specific pay data
Here’s what we found from the BLS on how average wages differ by industry – from lowest to highest:
Industry | Annual mean wage (USD) |
Arts, entertainment, and recreation | $31,760 |
Accommodation and food services | $34,900 |
Retail trade | $36,700 |
Administrative and support and waste management and remediation services | $38,950 |
Other services (except federal, state, and local) | $39,840 |
Health care and social assistance | $41,940 |
Real estate and rental and leasing | $43,060 |
Cross-industry, private, federal, state, and local government | $43,520 |
Educational services | $44,230 |
Federal, state, and local government, excluding schools, hospitals, and the United States Postal Service (USPS) | $45,330 |
Construction | $46,110 |
Professional, scientific, and technical services | $46,260 |
Transportation and warehousing | $46,500 |
Agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting | $46,840 |
Finance and insurance | $47,590 |
Wholesale trade | $48,160 |
Management of companies and enterprises | $49,160 |
Manufacturing | $50,790 |
Information | $51,900 |
Mining | $53,040 |
Utilities | $60,520 |
5 highest-paying industries
Industries with high revenues and profits, specialized skill needs, and strong demand for CSRs tend to pay them more.
Below are the top-paying industries and our analysis of why they pay well.
Utilities: This industry includes power generation, water and sewage systems, and natural gas distribution. As such, CSRs in utilities often manage critical accounts and resolve billing disputes or outages for essential services like electricity and water. The complexity and urgency of these issues justify higher pay compared to less specialized industries.
Mining: Mining businesses – especially in oil and gas extraction, where the annual mean wage is $64,170 – pay CSRs well because they coordinate logistics and compliance documentation. The CSR role often requires mining industry-specific knowledge, which further contributes to above-average wages.
Information: CSRs in the information industry frequently handle digital platform subscriptions, software troubleshooting, and technical inquiries. This requires specialized tech support training, which increases salaries compared with non-specialist CSR roles.
Manufacturing: CSRs in this industry support clients with order tracking, supply chain coordination, and technical product inquiries. They often navigate complex systems and meet tight deadlines, which enhances their baseline salary expectations against CSRs in lower-paying industries.
Management of companies and enterprises: CSRs working with management generally liaise between corporate clients and executive teams. This requires advanced communication and organizational skills – which most typical frontline CSR staff won’t have. These expert CSRs also frequently handle high-stakes accounts, resulting in higher compensation.
5 lowest-paying industries
Sectors that solve more straightforward customer queries – or rely on slimmer profit margins (and therefore tighter budgets) – tend to pay CSRs less.
Here are the five lowest-paying industries for customer service representatives and the reasons why:
Arts, entertainment, and recreation: CSRs in this industry often handle simpler tasks like ticket sales and membership inquiries. These roles typically require general customer service skills rather than specialized expertise, and the seasonal or part-time nature of many jobs in this sector keeps wages lower. Casinos, museums, and travel accommodations (like hostels and campsites) generally operate on lower profits and unstable revenue streams, meaning wages will also be lower.
Accommodation and food services: CSRs in this sector manage bookings, reservations, and customer inquiries. High turnover rates and reliance on entry-level skills – combined with tight profit margins typical of the hospitality industry – mean less money in CSRs’ pockets.
Retail trade: Retail CSRs primarily assist customers with purchases, returns, and product inquiries. The high volume of entry-level workers and minimal technical skill requirements often result in reduced pay.
Administrative & support and waste management & remediation services: In these sectors, customer service representatives typically support administrative operations or handle scheduling. The focus on cost-saving measures also often leads to compressed wages for these roles.
Other services (except federal, state, and local): This diverse category includes repair and maintenance, personal and laundry services, and religious, grantmaking, civic, professional, and similar organizations. CSRs might handle customer inquiries for services like repairs, dry cleaning, or nonprofit activities. Localized operations, small business budgets, or nonprofit funding constraints limit pay. Most of these roles also prioritize basic interpersonal skills over technical expertise – meaning lower pay.
Pay by experience and education
Here’s how CSR salaries can differ by experience and education:
Average wage by years of experience
Entry level (0-1 year): $36,000-$51,000 per year
Mid-career (4-6 years): $36,000-$53,000 per year
Experienced (10-14 years): $37,000-$55,000 per year
Certifications to improve earning potential
According to the BLS, the entry-level education required for CSRs is a high school diploma or equivalent. But there are some additional credentials that can help boost CSRs’ pay. These include:
Certified Customer Service Professional (CCSP): The National Customer Service Association (NCSA) offers this certification to help people enhance their customer service skills and knowledge. Training focuses on key areas like communication, problem-solving, and service strategies to improve customer satisfaction. Candidates learn how to deliver exceptional service and handle different customer scenarios.
HDI Customer Service Representative (HDI-CSR): HDI offers a certification for CSRs engaging directly with customers in a support center or service desk environment. HDI-CSR confirms CSRs’ skills in problem-solving, communication, driving service excellence, and process mastery.
Customer Service Representative (CSR) Certification: The International Customer Service Association (ICSA) offers a certification to help equip CSRs with the skills and knowledge required to excel. This includes communication techniques, problem-solving strategies, and customer satisfaction principles.
Certified Client Service Professional (CCSP): The Professional Association for Customer Engagement (PACE) offers CSRs the chance to develop and validate their expertise in client engagement. It focuses on service skills, knowledge of best practices in customer interactions, and the ability to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
6 key benefits beyond salary for CSRs
When evaluating job offers, the best customer service representatives consider more than just salaries. You’ll want to offer attractive benefits to grab their attention.
Consider including these benefits in your compensation package:
Health insurance: Providing comprehensive health plans, including vision, dental, and life insurance, demonstrates a commitment to CSRs’ well-being.
Paid time off (PTO): Offering paid leave – like vacation days, mental health days, and sick leave – helps CSRs recharge and reduces burnout from managing high volumes of customer interactions.
Retirement plans: A 401(k) plan or similar option appeals to CSRs planning for the future. Offer one to show you’re committed to their long-term stability.
Flexible and remote work: CSR roles are primed for remote work, so offer flexible schedules or hybrid options and see your talent pool expand.
Learning and development opportunities: When deciding on a complete package, consider funding certifications like the Certified Customer Service Professional (CCSP) or training in advanced communication skills for candidates.
Additional perks: Childcare assistance, commuter benefits, and wellness programs are perfect for customer service representatives who must balance work and personal responsibilities. They’ll help you stand out as an employer CSRs want to work for.
Hire the best customer service representatives with TestGorilla's talent assessments
Salary benchmarks for customer service representatives help you determine the right offer for your open role. But when it comes to making that final offer, customer service candidates’ real-world skills and abilities need to align with what you’re giving them. You want to pay fairly, but you also need a good return on investment.
TestGorilla’s library of 350+ science-backed talent tests helps you evaluate your CSR candidates as deeply as possible before making an offer. Combine up to five tests to create a custom CSR assessment.
Get started with some different tests below:
Role-specific tests
Zendesk CS test
Hubspot CRM test
Cognitive and soft skills
Problem Solving test
Communication test
Attention to Detail (Textual) test
Verbal Reasoning test
Personality and culture
Culture Add test
DISC test, Enneagram test, and other personality tests
Motivation test
These assessments – paired with the right customer service interview questions – help show what candidates bring to the table. For CSR roles, that means anything from problem-solving, communication, and software skills to motivations, working preferences, culture add, and more.
Sign up for a free account or schedule a live demo with TestGorilla today.
FAQs
What must a customer service representative have?
Good customer service representatives are empathetic, adaptable, and strong communicators. Relationship-building, problem-solving, and efficiency form the backbone of this role and its responsibilities. However, these professionals often also need product knowledge and digital literacy.
What are three things customers want from customer service?
Three things customers want from CS are highly-trained, knowledgeable staff; quick, quality response times; and proactive issue resolution across all touchpoints.
You've scrolled this far
Why not try TestGorilla for free, and see what happens when you put skills first.