How to eliminate disparate impact practices and disparate treatment
Table of contents
Disparate impact and disparate treatment, also known as adverse impact and adverse treatment, are discriminatory practices that lead to inequality and harm organizations and employees.
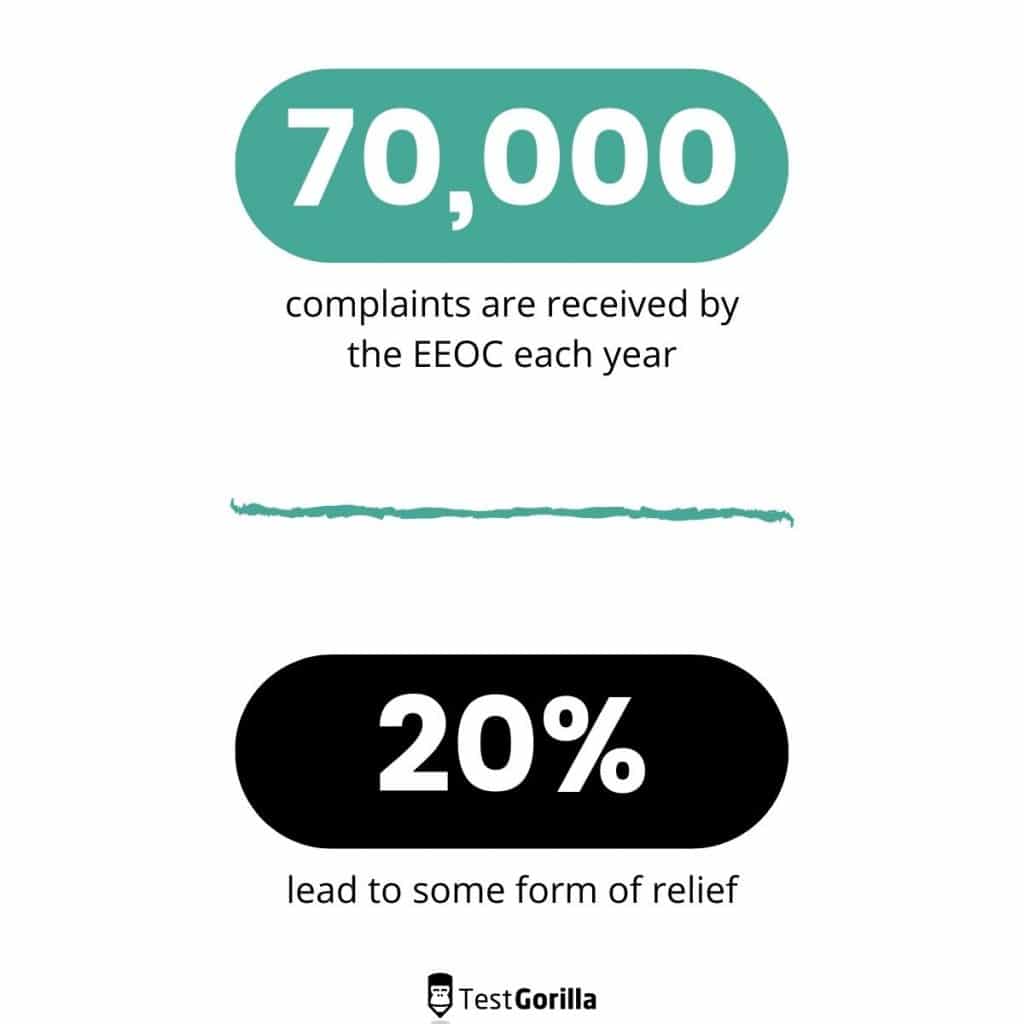
Although workplace discrimination is illegal, it’s still a major problem in the US and in most other countries. Each year, the US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) and its local agencies receive over 70 thousand complaints, most of them for racial discrimination, while approximately 20% receive some form of compensation or relief.
Disparate treatment is a form of intentional discrimination based on race, color, sex, age, gender identity, sexual orientation, religion, disability, or country of origin. If you deliberately treat someone differently based on any of those characteristics, this is disparate treatment.
Disparate impact, on the other hand, is an unintentional action or policy that leads to the discrimination of a group of individuals. Disparate impact can sometimes be justified if it’s related to the requirements of a specific position. For example, if a company administers a test to check applicants’ reaction time and eye-hand coordination, this might lead to the disproportionate disqualification of older candidates. If, however, this is a job requirement (say, for example, for an air traffic controller), it makes it a necessity that the employer must take into consideration.
In most cases, however, the disparate impact is unrelated to business needs. Both disparate impact and disparate treatment can create a workplace environment that isn’t welcoming and supportive, and that, ultimately, leads to a worsening performance of different teams and of the entire company. Therefore, organizations need to make sure that:
Their hiring procedures do not lead to discrimination, be it intentional or unintentional.
They’re hiring a diverse workforce
That they treat all employees equally, both in day-to-day operations and regarding bigger initiatives.
This will lead to an improved overall performance: companies whose top priorities include inclusivity and diversity perform better and are more capable to attract and retain top talent.
What are some examples of disparate impact and disparate treatment?
Let’s look at examples of disparate impact and disparate treatment before we move on to discuss what you can do to avoid both at your organization.
Examples of disparate impact
Interviewer bias can affect hiring outcomes and lead to unfair treatment of a group or a minority. Interviewer bias has many forms and isn’t always easy to detect. Eliminating stereotyping, or gender and racial bias might be the obvious (and necessary) first step. However, you could also fall prey to other types of biases, such as, for example:
“Like me” bias, or hiring based on similarities with the applicant that are irrelevant to the position.
Cultural bias, or making a hiring decision based on the candidate’s culture.
Non-verbal bias, where the applicant’s body language affects your decision.
Hiring tests that disproportionately disqualify candidates of a given race, sex, religion, or who share other characteristics, are also a form of disparate impact. For example, if you administer a hiring test that eliminates all Hispanic women, that’s the disparate impact (and a discriminatory practice).
Examples of disparate treatment
Discrimination based on race, color, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, disability, and other characteristics is, unfortunately, still present at many organizations. If you administer an additional test to someone based on their gender or do an additional phase of screening only of those candidates who have a Middle Eastern-sounding name, this is a form of disparate treatment. If a specific group is singled out and treated differently, this is a form of disparate impact. Disparate treatment isn’t easy to prove, as employers won’t openly admit to discriminatory practices, and courts require substantial proof of a hostile workplace environment, but lawsuits can be very costly for companies. For example, FAPS, Inc., a company in Port Newark, paid a $350,000 settlement in an EEOC lawsuit from 2016, for refusing to hire qualified African-American candidates and relying on a word-of-mouth hiring, resulting in a predominantly white workforce in a racially diverse area.
What can you do to eliminate disparate impact and disparate treatment at your organization?
There are different methods that can help you eliminate disparate impact and disparate treatment at your organization. In order for them to be effective, however, everyone needs to be on board and understand the importance of getting rid of discriminatory practices.
Make sure you have a fair hiring process
The first step is to make sure that you have a fair hiring process in place, that your job ad is clear and inclusive, that you treat all applicants equally.
In your job ad, write a clear description of the position & the required skills—if you’re vague in it, this leaves lots of space for bias and can lead to making a hiring decision based on personal preferences, rather than on capabilities. Make sure that your ad is gender-neutral, as well.
Another way to eliminate discrimination is to administer skills tests to test candidates’ skills and knowledge and automate a part of your hiring process. Tests help you make sure you’re hiring based on qualifications, and that you’re eliminating noise and irrelevant information during the initial selection. You can anonymize tests to further reduce bias.
You can test for many skills, including technical skills, cognitive capacities, language proficiency, and more, such as debugging in JavaScript, UX/UI design, and French.
The next step would be to screen candidates on the phone: this way, you don’t get all the non-verbal cues you have at the video or in-person interviews and you cannot be biased based on their appearance. Make sure that you take detailed notes, in order to limit recency bias, or preferring someone simply because you remember them better.
Structured interviews come next, and according to Iris Bohnet for Harvard Business Review, they are an important element in a successful and unbiased hiring process. Interviews should include the same set of questions in the same or similar order, and leave no place for small talk.
During the hiring process, you need to document everything consistently. Take detailed notes, so you can compare candidates without relying on your memory, and without falling prey to subjectivity.
Have equal treatment policies in place
To eliminate disparate impact and disparate treatment, everyone needs to be treated equally at all times. Make sure you have transparent procedures for hiring, firing, and laying off employees.
Give everyone equal access to information and make sure you’re not excluding employees from important discussions. Ensure equal access to promotion opportunities, and establish a clear set of rules and define what good performance is, and how it’s measured. All employees need to have the right conditions to perform well, and creating an inclusive and supportive work environment is key for that.
Educate both your hiring team and your management on discrimination and unfair hiring and employment practices
The company’s management needs to be fully involved and onboard, in order for your efforts to be effective. Educate your team on unfair hiring and employment practices, and actively discuss topics like unintentional discrimination and unconscious bias, to make sure that everyone is on the same page.
Questions about age, sexual orientation, civil status, state or country of origin, for example, simply have no place at an interview, and your hiring committee needs to be aware of that.
The best insights on HR and recruitment, delivered to your inbox.
Biweekly updates. No spam. Unsubscribe any time.
Eliminate disparate impact and disparate treatment to improve your work environment and make better hires
Discrimination can affect your organization negatively in many different ways and can have many forms, some of them subtler than others, and almost invisible. Intentions are not the only thing that matters, in this case: keeping unconscious bias and disparate impact in check is equally important as eliminating intentional discrimination.
There are many measures you can take to eliminate disparate impact and disparate treatment from your organization. Automating a part of your hiring process can help reduce bias and make your organization more inclusive, and hire for skills, regardless of background and origin. As a result, it’ll be much easier to hire and retain highly skilled employees.
Structured interviews, especially if you combine them with skills tests, can further help you make informed, data-driven, and unbiased choices.
Creating clear, transparent procedures also helps you guarantee that everyone is treated fairly and that you’re providing equal opportunities to all applicants, and hire diverse talent coming from different paths of life.
Related posts
You've scrolled this far
Why not try TestGorilla for free, and see what happens when you put skills first.