Diversity and inclusion metrics 2023: What you need to know
In 2020, conversations about diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) were accelerated thanks to the pandemic, protests in the US, and the global economic crisis. According to Gartner, between 2017 and 2020, the demand for recruiters with diversity hiring experience jumped by 800%.
Although a lot of businesses have devoted their time and resources to invest in DEI in the workplace, hiring managers also need to know how to measure the effectiveness of these endeavors. Otherwise, your efforts to make the company diverse and inclusive may fail.
DEI metrics refer to a set of metrics that organizations use to track their progress and success in promoting DEI within their workforce and broader operations. This can help them identify areas where they need to improve and measure the effectiveness of their DEI initiatives.
In this article, we look at what DEI metrics are and why they are important. We’ll also discuss nine key metrics that will give you insights into how inclusive your workplace is.
What are DEI metrics?
As mentioned, DEI metrics are a way to track the effectiveness of your organization’s DEI efforts.
Knowing what to look for and how to measure it enables you to reach your diversity goals quicker and make improvements where necessary. The metrics we’ve compiled here measure the employee’s lifecycle from hiring to retention, their job satisfaction and opportunities for advancement, and how well the business is represented by its suppliers and leadership.
Depending on your company’s size, some metrics might be more applicable than others. On the whole, you want to use these metrics to pinpoint important areas that need your attention and urgent improvement. Others may require you to develop a long-term strategy for development and refinement.
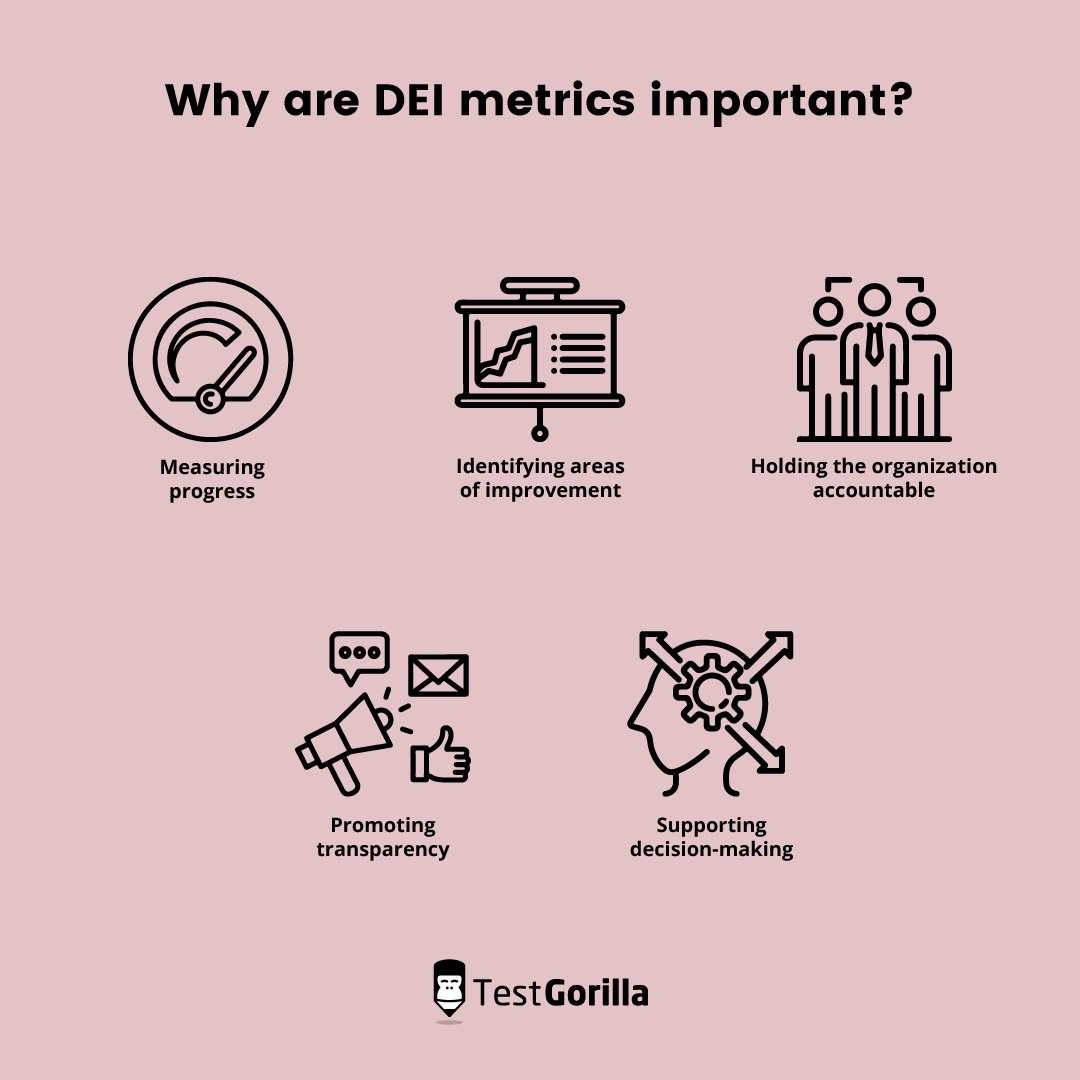
Why are DEI metrics important?
Metrics for diversity and inclusion are important to track for several reasons:
Measuring progress: DEI metrics provide a way to track your progress toward creating a more diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplace. Without metrics, it’s difficult to know whether diversity and inclusion efforts are making a meaningful impact.
Identifying areas of improvement: By tracking DEI metrics, organizations can identify areas where they need to improve. For example, if the data shows that women or people of color are underrepresented in leadership positions, the organization can take steps to address this.
Holding the organization accountable: DEI metrics provide a way to hold the organization accountable for its diversity and inclusion efforts. By tracking these metrics, stakeholders, such as employees, customers, and investors, can see whether the organization is making progress toward its stated DEI goals.
Promoting transparency: DEI metrics promote transparency by making diversity and inclusion data available to stakeholders. This can help build trust and credibility with employees and investors.
Supporting decision-making: DEI metrics can support decision-making by providing data-driven insights. For example, if the data shows that women are leaving the organization at a higher rate than men, the business can use this information to develop strategies to retain female employees.
Now that you know what DEI metrics are and why they’re important, let’s discuss nine diversity and inclusion metrics you can use to track and monitor your progress in 2023.
9 DEI metrics to monitor
DEI metrics can be tricky to monitor if you don’t know how to use them correctly. To make it easier to understand these metrics, we’ve divided them into three different categories: employee lifecycle, employee experience, and company representation.
Each category breaks up the DEI metrics into smaller parts, enabling you to better understand them and focus on each one separately.
Employee lifecycle
Your employee’s lifecycle in the business includes metrics such as hiring, representation, and retention.
1. Hiring
Your company’s diversity starts with the hiring process.
According to a study done by the National Bureau of Economic Research, applications sent by fictitious candidates with distinctively Black-sounding names were 2.1% less likely to result in contact from the employer than those with White-sounding names.
It also found a between-company standard deviation in gender contact gaps of 2.7%, meaning some companies favor male applicants and others female applicants.
To evaluate how well you perform when it comes to hiring diverse talent, you need to turn your attention to two main factors:
How diverse your hiring panel is
How diverse your talent pool is
A diverse hiring panel minimizes unconscious hiring bias, enabling you to attract a more diverse talent pool with a wider range of backgrounds, sexes, genders, religions, sexual orientations, and more. You need to pay close attention to these two factors to ensure you stay on top of your DEI hiring metrics.
To make your hiring process more diverse, you can commit to blind hiring and use the right diversity hiring tools.
Want to get more value from your recruitment?
Our complete blueprint will provide the tips, strategies, and insights you need to maximize your recruitment ROI.
2. Demographics
Your company makeup is an important diversity and inclusion metric.
You might be surprised how many businesses are diverse at an employee level but less so among upper management. This is why it’s critical to track the demographics across your company, from employees to managers and even the C-suite.
To do this, you can take the total number of employees in the business and divide it by the number of employees in a particular group. Then you can make a table to see what percentages of each group are represented in your organization.
Tracking this metric helps you monitor changes in your company’s demographics. Let’s say you find out that LGBTQ+ employees made up 5.1% of your organization’s employees in 2021 but only 3.9% in 2023.
In this case, you could determine why that number went down and make adjustments to company policies if there was an issue with someone from that group in the past. You can do the same for other groups as well.
Finally, you can post your company’s demographics to your webpage to be transparent and show current and future employees that you’re serious about diversity in your organization.
3. Retention
Though having a diverse workforce will boost your productivity and innovation, you must also retain employees from diverse backgrounds and not just have them as a token of diversity.
Glassdoor reports that 47% of Black and 49% of Hispanic job seekers and employees quit a position after experiencing or seeing discrimination in the workplace, compared with 38% of White job seekers and employees.
Tracking and measuring employee turnover will show you how inclusive your company is. If more employees from diverse backgrounds are leaving, that is a clear sign something is amiss and needs to be corrected.
You can regularly send out surveys to collect feedback and find out how employees feel about their workplace and colleagues. Try to find discrepancies between what you think you know and what’s actually happening at an employee level and make corrections.
Employee experience
It’s hard to quantify employee experience, but nonetheless, it’s useful to collect data from your employees through surveys and build your own data. As a hiring manager, you should pay close attention to the following metrics:
4. Job satisfaction
Using surveys, you can gauge the overall employee satisfaction in your business. Some employees will report higher satisfaction rates than others. Analyze the data and see if unsatisfied employees belong to a specific minority group.
For example, if Asian employees report poorer self-satisfaction, you could look into how to promote their well-being better or see who’s been performing well and run them up for promotion.
Most importantly, try to pinpoint any underlying issues, like microaggressions or a specific cultural problem within the business. If you find such problems, you need to evaluate your company’s culture and values and put into place more stringent non-discriminatory practices.
5. Advancement in the workplace
Another key metric to monitor is the advancement rate of diversity groups in your organization.
You can measure this by looking at how many employees from minority groups have been promoted in a given period, such as the past 12 months. See if there’s a trend to promote only White male employees, and evaluate your promotion criteria.
For instance, McKinsey & Company reports that women are still underrepresented in leadership positions, despite the progress made by companies to change that. Women of color are even less likely to get promoted.
Of course, you should base your decisions on merit above all else. However, consider installing quotas for the promotion of women and other minority groups to even out discrepancies when it comes to advancement opportunities in the workplace.
6. Pay equity
The gender pay gap is a real issue among small and large companies alike.
Although that may not be true in your organization, it is something to keep an eye on. If there is such an issue, you should remedy it immediately.
To start, list all your employees, and then separate them by gender. Take the average hourly pay of the male employees and subtract the average hourly pay of the female employees from it. Divide that number by the male average hourly rate and multiply it by 100.
The resulting figure represents the gender pay gap in your business. You can do the same calculation for other minority groups in your organization.
Once you have these numbers, you can start thinking of solutions to close the pay gap among diversity groups.
7. Accessibility
Accessibility is another metric to be on the lookout for.
It is measured by how welcomed employees feel and whether they have the right tools and facilities to feel safe, included, and able to do their job. You can ask the following questions to determine how accessible your organization is:
Is your office building easily accessible for employees with disabilities?
Do you have facilities for breastfeeding mothers and baby rooms, and are your washrooms inclusive for all employees, regardless of gender?
Do you offer parental leave for both mothers and fathers?
Do you recognize all cultural and religious holidays and offer days off for those holidays?
Answer these questions to determine whether you offer equal accessibility for all employees. If you don’t, make the necessary changes.
Company representation
When it comes to diversity recruiting metrics, your company’s representation has an equally important role.
Don’t focus only on the employee level – zoom out and see how your business presents itself to the outside world. This includes your leadership and partner networks.
8. Leadership
As mentioned, companies are not as diverse at the leadership level as they are at the employee level.
According to McKinsey & Company, organizations that have diverse leadership can outperform those that do not by as much as 48%.
Using the demographics data you gathered, see how many employees from diversity groups are in leadership positions. If you’re struggling with underrepresentation, consider prioritizing your diversity at the management level.
9. Partners and suppliers
Finally, you need to see who your suppliers and partners are.
Do you collaborate only with certain suppliers, or do you have a diverse network? You may be missing out on services that your current suppliers are not delivering.
Evaluate your networks and the people your business is doing work with to ensure there’s no bias in the selection process. This way, you can give small business owners and underrepresented businesses more opportunities and drive real change both across and outside your company.
The best insights on HR and recruitment, delivered to your inbox.
Biweekly updates. No spam. Unsubscribe any time.
Become a successful organization by measuring your DEI metrics
Though you may be doing a lot to diversify your company, you cannot drive real change without measuring your progress.
If you don’t know how your employees are feeling and what their concerns are, your DEI efforts will fall flat. That is why using the DEI metrics outlined in this article to track your progress will help you to become a more successful organization.
On a final note, you need to use the right tools to hire without bias. offers dozens of pre-employment evaluations that will help you find the right talent, regardless of their background.
You can start your free plan or request a live 30-minute demo with one of our experts to see which plan and tests will be most useful for you.
Sources
Bryan, Jordan. (February 3, 2021). “How 2020 Accelerated Conversations on Diversity, Equity and Inclusion”. Gartner. Retrieved March 7, 2023. https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/how-2020-accelerated-conversations-on-diversity-equity-and-inclusion
Zuech, Teresa. (December 9, 2020). “Use Data to Inform Diversity Hiring Decisions”. Gartner. Retrieved March 7, 2023. https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/use-data-to-inform-diversity-hiring-decisions
Related posts
You've scrolled this far
Why not try TestGorilla for free, and see what happens when you put skills first.