20 technical business analyst interview questions to ask job applicants
Business analysts work with data to create business insights and identify problems in staff development, organizational challenges, or IT processes. Their duties involve improving a company’s operations and chances in a highly competitive market. These agile professionals require strong technical skills to deliver data-driven suggestions.
One way to identify candidates with technical skills is to send them an IT Business Analyst test. Your job applicants’ results should prove they can handle requirement analysis and business change management.
Hiring candidates doesn’t have to be challenging when you have the right skill tests and interview questions. Discover 20 technical business analyst interview questions and sample answers to help you compare their responses.
20 technical business analyst interview questions about skills and standard processes
Use these 20 technical business analyst interview questions to determine which candidates have the most knowledge. Pairing these questions with pre-employment technical tests and behavioral interview questions for business analysts can help you find top talent for your company.
1. What is the purpose of UML? How do you use it?
UML stands for unified modeling language, which is a general-purpose visual language that helps software developers create new systems. It includes a collection of engineering practices, such as diagrams and coding implementation, to support object-oriented software development.
Business analysts will use modeling languages to streamline workflow and improve company processes, whether calculating financial data or identifying potential security risks. Experienced candidates may know how to use a UML diagram when planning to organize a workspace.
Send candidates a Data Modeling Concepts test to learn more about their technical skills and knowledge of conceptual, logical data modeling.
2. What is the purpose of the requirement traceability matrix?
A requirement traceability matrix is a document that tracks user conditions in user cases. It shows requirements related to artifacts, which are byproducts of a software model. Data analysts can use this document to ensure your company meets all client and market requirements. They might conduct a test case to examine your monthly deliverables.
3. Define business modeling.
Candidates should understand business modeling if they’re passionate about enhancing your company. This step-by-step approach describes how a company defines values in economic, social, and cultural contexts.
Technical professionals must have strong analytical skills to improve your company’s investment, talent recruitment, and staff management.
Business analysts will use the following attributes when developing a strategic plan:
The overall vision of the company
Short- and long-term mission
Primary objectives
Business strategies
Final action plan
Use a Business Judgment test to determine whether candidates can create valuable strategies when improving your company’s competitive position.
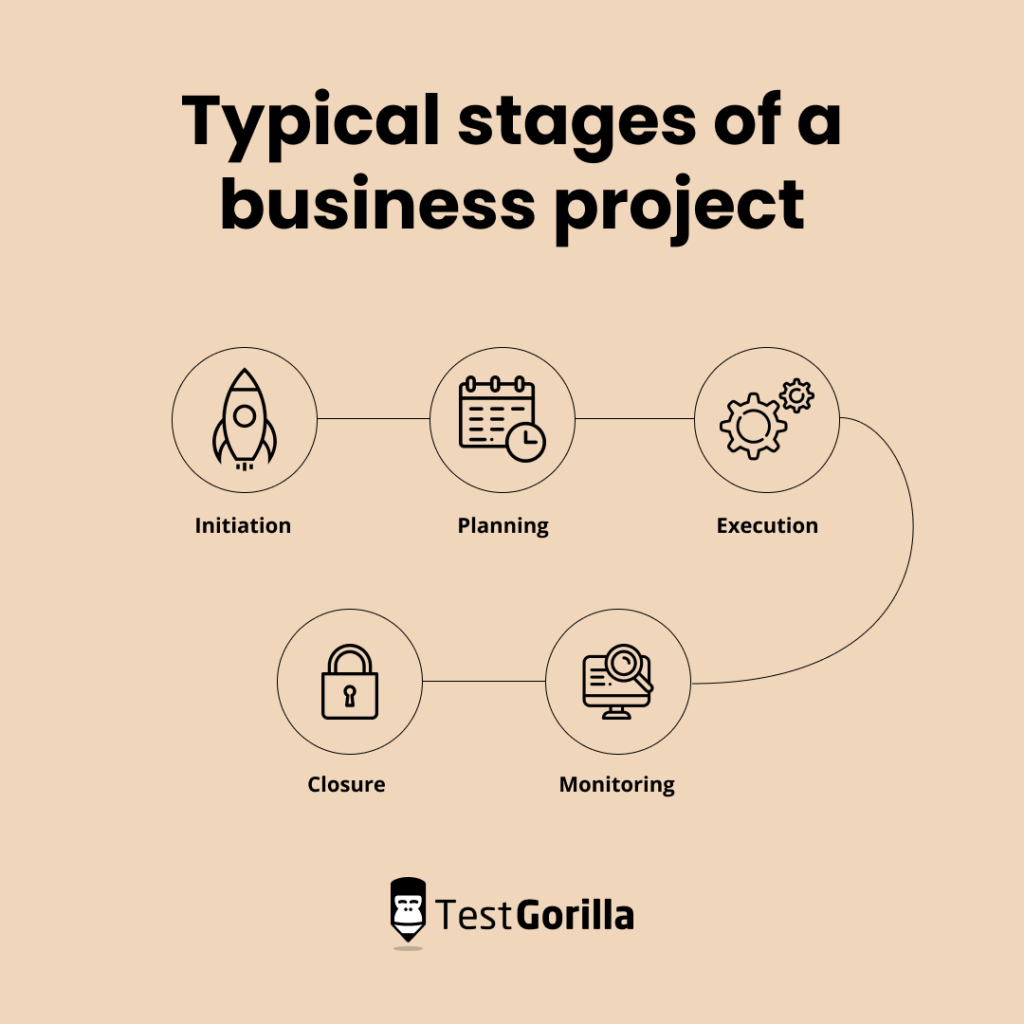
4. Name the various stages of a business project.
A business project can help a company achieve objectives and improve its position in the market. To create this plan, business analysts must follow five steps that involve planning and execution.
Some typical stages of a business project include:
Initiation: This is the first step in building a strategy to help the company deliver assets to stakeholders, employees, or customers. A business analyst will meet with the team to explore and examine the project’s feasibility.
Planning: Once everyone agrees on an idea, the planning stage begins. This phase involves a work breakdown structure (WBS), which is a tool that assigns deliverables to team members and lists available resources to the business analyst.
Execution: Project execution puts the plan into action. The company performs specific tasks to reach a desired outcome, such as designing a new marketing strategy.
Monitoring: After the team completes a project, the business analyst can collect and examine data to determine its success. This is a crucial stage because it allows analysts to identify problems and make adjustments before they cause damage.
Closure: Ending the project means communicating the outcome and final project disposition to clients. Participants can also write down their strong and weak points when navigating the project life cycle.
5. Describe the diagrams you would use as a business analyst. How do they influence your work?
It’s worth asking this question to determine whether candidates can use standard business analysis documents when creating a user case.
Many complex diagrams help business analysts collect data. The principal diagrams a business analyst would use include:
Flowcharts: A flowchart depicts the complete workflow of a project or business operation, which makes it easier for external stakeholders to examine the process during development.
Use case diagrams: Business analysts use these diagrams when showing the set of actions, functions, features, and services a project needs to have.
Collaboration diagrams: In a unified modeling language, the collaboration diagram shows the relationship between objects. However, a business analyst may use it to determine the interactions between your company’s workflow and output productivity levels.
6. What is BRD? How is it different from SRS?
BRD stands for business requirement document, a formal report showing the project objectives, business strategies, and desired outcomes. A company and external client can refer to this document throughout project development.
On the other hand, SRS is a software requirements specification that represents the purpose and environment for developed software processes. The difference is that stakeholders use BRD for quality assurance and technical leads, and small and medium-sized enterprises use SRS for data governance.
Send candidates an Exploratory Data Analysis test to see how they extract data visualizations using documents such as BRD. This assessment is an efficient way of testing candidates’ business analyst skills.
7. What are the exception and alternate flow in a use-case diagram?
Alternate flow shows the sequence of steps in a use case that helps a company meets its goals. It usually means a user has taken an alternate path in business process modeling to optimize workflows better.
Exception flow refers to an unintended path due to insufficient resources or missing information. This undesirable sequence of steps also depicts how a process can fail and create errors that require urgent mitigation. Most of the time, exception flow doesn’t achieve the main goal in a business case.
8. Define analytical reporting.
Candidates must understand analytical reporting when managing data and using business intelligence to gain control over a company’s processes. This question can also help you better understand their data science skills in data visualization and business process improvement.
Analytical reporting is the process of evaluating a company’s strategies and decisions based on key data insights. Business analysts must write this report to assess your course of action with deliverables. For example, these professionals can offer suggestions on how to expand your products into a larger market.
From 2022 onwards, more companies require business analysts to conduct process mapping and provide data-driven decision-making. Therefore, hiring candidates with strong analytical skills is essential.
9. What is scope creep? How can you avoid it?
Scope creep refers to sudden changes, requirements, or uncontrolled growth due to a project not having a comprehensive plan. Without proper planning, it’s easy for a company to miss functional needs such as product features. Avoiding this problem can be challenging, but experienced candidates should know that tracking a project’s objectives is critical.
Business analytics can avoid scope creep by noting down project requirements. Keeping the requirements available ensures the company meets all standards. Improving communication between team members will also provide clarity when creating a project charter.
Consider sending candidates a Communication Skills test to determine whether they can communicate problems and explain the client acceptance criteria to team members.
10. Explain non-functional requirements and how you capture them.
Non-functional requirements are conditions a company must meet to be successful. These conditions usually cover performance, security, scalability, and usability.
A system or project can work without non-functional requirements but won’t satisfy a client’s expectations or standards. Therefore, it’s essential to capture important attributes by using scenarios, which are stories that represent a project’s performance in real life. For instance, one requirement states that a blog must meet the web content accessibility guidelines.
11. What does INVEST stand for?
INVEST stands for independent, negotiable, valuable, estimable, sized-appropriately, and testable. These aspects can help business analysts determine the future success of a project or system.
Candidates might also provide the following definitions:
Independent: The user story should be self-contained to avoid dependency on other descriptions of the same project.
Negotiable: Business analysts may use the agile methodology to increase flexibility in a project, meaning that team members should be able to discuss potential changes or adaptations during development.
Valuable: It’s essential that user stories provide value to a customer or client. Values represent the importance of specific features and how a company can continue to strive for efficient functionality.
Estimable: A business analyst and developer must know how to implement an idea. User stories also need to be small to allow analysts to estimate their overall success.
Sized-appropriately: Teams should understand how big the user story must be when conducting an analytical report.
Testable: User stories are testable if the business analyst writes non-functionality requirements correctly. For example, “the blog page must load quickly” won’t be testable. Instead, the requirement “pages should load within five seconds 96% of the time” is better for smooth development and user acceptance testing (UAT).
Use a Working With Data test to see how candidates perform basic data analysis using the INVEST method.
12. How do you perform requirement gathering?
Requirement gathering involves identifying the project’s specifications from beginning to end. A business analyst will need this exploratory process to ensure your company meets client standards.
Common ways to perform requirement gathering include to:
Conduct interviews
Interview focus groups
Complete online surveys
Analyze documents
Interviews are one of the best methods because they foster open communication between the company and the user. However, these meetings can be expensive when speaking to a large group. Surveys are better for gathering large amounts of information from different audiences.
Send candidates a Market Research test to learn more about their research initiation and planning when gathering user requirements.
13. What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study determines how viable a project or idea is. Business analysts conduct this study during early development to identify potential issues and questions, meaning the company can address them quickly. Also, finding the advantages and disadvantages of a project is essential because it reveals improvements.
Companies should always address the following questions:
Does your company have enough tools, resources, and technology to complete the project?
Will your company have a reliable investment when producing a high return rate?
14. Name some of the tools you would use in business analytics.
Business analysts will use plenty of tools when managing data in a company. Therefore, having the technical skills to complete specific tasks is essential. You can determine whether candidates have enough work experience and knowledge to use complex tools in your team.
Some standard business analytics tools include:
Microsoft Excel
Tableau
Google Analytics
MicroStrategy
Qlik Sense
Microsoft Power BI
IBM Cognos Analytics
Dundas Data Visualization
Splunk
Since Excel is a popular tool in this technical industry, it’s worth sending candidates a Microsoft Excel test to see how they analyze data and complete calculations using extensive graphs.
15. How do you analyze performance metrics?
Performance metrics are types of measurable data that business analysts use to track a company’s processes. A KPI (key performance indicator) measures a specific area involved in project development and management. Using these metrics is important because they support strategy implementation when meeting long-term goals.
Four performance metrics candidates could mention include:
Business: This metric focuses on sales, marketing, and profitability when achieving objectives.
Sales: Daily sales numbers and lead generation percentages show the success of your products with customers or clients.
Project management: Business analysts can see how your company aims to stay within the timeline and budget of upcoming projects, including satisfaction metrics regarding customer-driven data.
Employee performance: A business analyst can determine your company’s productivity levels and whether improvements are necessary. For instance, they could measure the quantity and quality of specific work to see if professionalism is dropping.
16. What is gap analysis?
Gap analysis is a process that helps companies measure their performance in achieving business goals. Business analysts will use this assessment to find improvements or risks that could damage your brand’s reputation. These professionals can measure success in a few ways, but candidates should understand the basic steps in analyzing goals and business processes.
The steps for conducting gap analysis include to:
Identify the goals and areas to analyze in the company
Create short- and long-term plans that improve employer branding
Analyze existing processes to determine whether they meet goals
Compare those processes with the prospective plans to find ways for the company to efficiently improve
Define the gap and state the difference in quantifiable figures
Summarize improvement suggestions and create a final plan to bridge any outstanding gaps
17. What are the core competencies of a business analyst?
This question determines whether candidates have the right skills and personality to succeed in the open position. If they don’t know how a business analyst should interact with team members or perform their duties, they might not personally grow in your company.
Some core competencies of a business analyst include:
Advanced active listening skills
Knowledge of tasked objectives
The ability to arrange and host a meeting with stakeholders
Excellent time management and document preparation skills
A solid understanding of business management
Written and verbal communication skills
18. Define the term application usability.
Application usability measures the efficiency, effectiveness, and customer satisfaction of the company’s product. Candidates should understand that this term often applies to interactive user experience, which focuses on business systems, blogs and website pages, and mobile applications.
19. How do you manage frequently changing customers’ requirements while developing a system?
Sometimes, customers and clients can change their requirements during development. Adapting to these sudden changes is essential when producing a high-quality product or service.
A business analyst should write a document covering the number of changing requirements a client can make, including a certain point in development that the company won’t accept more amendments. The client should sign this contract to ensure both parties are on the same page.
It’s also necessary to note down any new requirements and how they will affect the company’s finances, resources, and timeline for the project.
20. How do you measure the quality of a product?
Measuring the quality of a product is essential for workflow analysis. It allows team members to consider their personal development processes and how they impacted the product’s success or outcome. Also, product measurement encourages the company to continuously improve its employer branding when attracting new customers and potential employees.
A business analyst can measure the quality of a product by following these key metrics:
Defect rate in the development cycle
Business process and test automation
The time it takes to rebuild a failed project
Speed of development
Quality of acceptance criteria when meeting customer expectations
When should you use technical business analyst interview questions in your hiring process?
Using technical business analyst interview questions after skill tests ensures you’re interviewing the right candidates. Skill tests give you more insight into candidates’ work experience and skills, as they will answer questions regarding their knowledge of business analytics.
All you need to do is choose an assessment name, create custom questions, and send the test to each candidate. Once they have finished, you can compare their answers to determine which job applicant best suits your open position. It’s a simple process that enhances your hiring process.
Skills-based hiring is the future of employment because it allows companies to fill talent gaps with professionals.
The best insights on HR and recruitment, delivered to your inbox.
Biweekly updates. No spam. Unsubscribe any time.
Use our technical business analyst interview questions and skill tests to hire professionals
Before starting your hiring process, look through our comprehensive test library to find relevant skill assessments. There are more than 300 tests to choose from, covering personality, cognitive function, business judgment, typing speed, and more. You can also preview the questions to determine whether the test suits your open position.
For more guidance on skill tests, book a free demo with us to learn more about our screening tools. Discover why skill assessments reduce unconscious bias, promote employer branding, and improve recruitment.
Related posts
You've scrolled this far
Why not try TestGorilla for free, and see what happens when you put skills first.