VR training: A guide for HR professionals looking to modernize learning and development
Virtual reality, or VR, is changing how companies train their employees. More than 50% of businesses are in the process of bringing VR on board – with 21% already using the tech to support staff.[1]
Immersive VR training provides safe, risk-managed, and affordable opportunities for motivated employees to practice complex techniques and gain confidence.
What’s more, companies are training learners much faster through VR compared to classroom studies, and workers are considerably more focused.
Ignore this emerging HR technology trend, and you risk falling behind competitors with more confident, productive, and flexible talent.
In this guide, we show you why VR training is such a game-changer and how to use this HR technology to your advantage.
Table of contents
- What is VR training?
- Why is VR employee training important to HR professionals?
- The benefits of VR workplace training
- The top industries using VR to train employees
- 5 best virtual reality training tools
- 6 best practices for leveraging VR training in your HR department
- 3 examples of companies succeeding with VR training
- Embrace VR training and inspire more capable, confident employees
- VR Training FAQs
What is VR training?
VR training digitally simulates real-world scenarios employees face in their industry.
A VR program could simulate an emergency, a practical exercise using sensitive tools, or interactions with others, like clients and patients.
VR training provides 360-degree experiences through headsets and controllers that learners can use to interact with mock scenarios.
Companies frequently balance VR training in their HR tech stacks with theoretical practice and skills testing to appeal to different learning styles.
It’s an efficient addition to a hybrid work technology stack, too. Workers can train on the hardware in-house and then confidently use the techniques learned in the field.
Virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality
There are three different strands of XR, or “extended reality.” Here’s a quick glossary.
Type of extended reality | Quick summary |
Virtual reality (VR) | VR products offer fully immersive environments – they replicate your presence in a simulated world |
Augmented reality (AR) | AR offers real-world training with digital elements and objects overlaid – the user can't directly interact with them but gets a 360-degree view of objects and tools |
Mixed reality (MR), or hybrid reality | MR refers to experiences where digital elements are overlaid but interact with some physical world elements |
Why is VR employee training important to HR professionals?
VR tech development has taken decades to mature. It was only around 2015-16 that the technology started to enter mainstream consciousness.[2]
Around this time, business owners started considering ways to use the Metaverse for hiring, and from there, HR managers realized the benefits of virtual reality for training employees.
VR tech immerses learners in realistic situations where they can make mistakes without affecting a company’s bottom line or putting lives in danger.
This learning and development style particularly appeals to 20% of trainees considered kinesthetic. Kinesthetic people prefer learning by "doing" rather than reading material or following instructions.[3]
VR learning is considered a safety perk for learners in high-risk roles. In industries like construction and defense, where training on the job risks injury or worse, people have a safe environment to "play around" in to build confidence.
The thirst for VR education is only building. Between 2023 and 2030, Fortune Business Insights predicts a compound annual growth rate of 30.7%.[4]
The best insights on HR and recruitment, delivered to your inbox.
Biweekly updates. No spam. Unsubscribe any time.
The benefits of VR workplace training
Used effectively, VR workplace training:
Reduces human errors and training risks
Improves performance and boosts training engagement
Reduces training costs
Cuts down training and ramp-up time
Boosts learning retention
Let’s break these points down.
1. Reduces human errors and training risks
Human error poses a risk to life in hazardous jobs and to reputation in roles managing sensitive information. For example, human error is directly responsible for 82% of data breaches.[5]
In some of the most dangerous industries, employees are even at risk of injury or death during training due to accidents.
People working in iron and steel are at risk of slips and falls, logistics drivers are at risk of traffic accidents, and construction workers could hurt themselves from falling or using tools.
The fatal injury rate in construction is around 23 people per 100,000, and non-fatal injuries affect 2.3% of employees.
With a VR training program, employees experience realistic working scenarios and practice their theoretical knowledge without harming themselves, hurting others, or causing damage.
Moreover, research into virtual reality simulation training for orthopedic surgeons found that trainees made half the critical surgery mistakes of non-VR learners.
2. Improves performance and boosts training engagement
Research shows people engage better when learning with VR than through traditional means.
V-learners, as PWC refers to them, are 3.75 times more emotionally connected to VR learning content than classroom trainees.
V-learners are also 2.3 times more engaged and four times more focused than e-learning trainees, making a firm case for blending learning management systems with VR.
People feel more engaged when learning via VR because they see how their theoretical learning applies in practice.
Rather than struggle on the job, employees could ask for advice and guidance now and hit the ground running faster when they start real-world work.
3. Reduces training costs
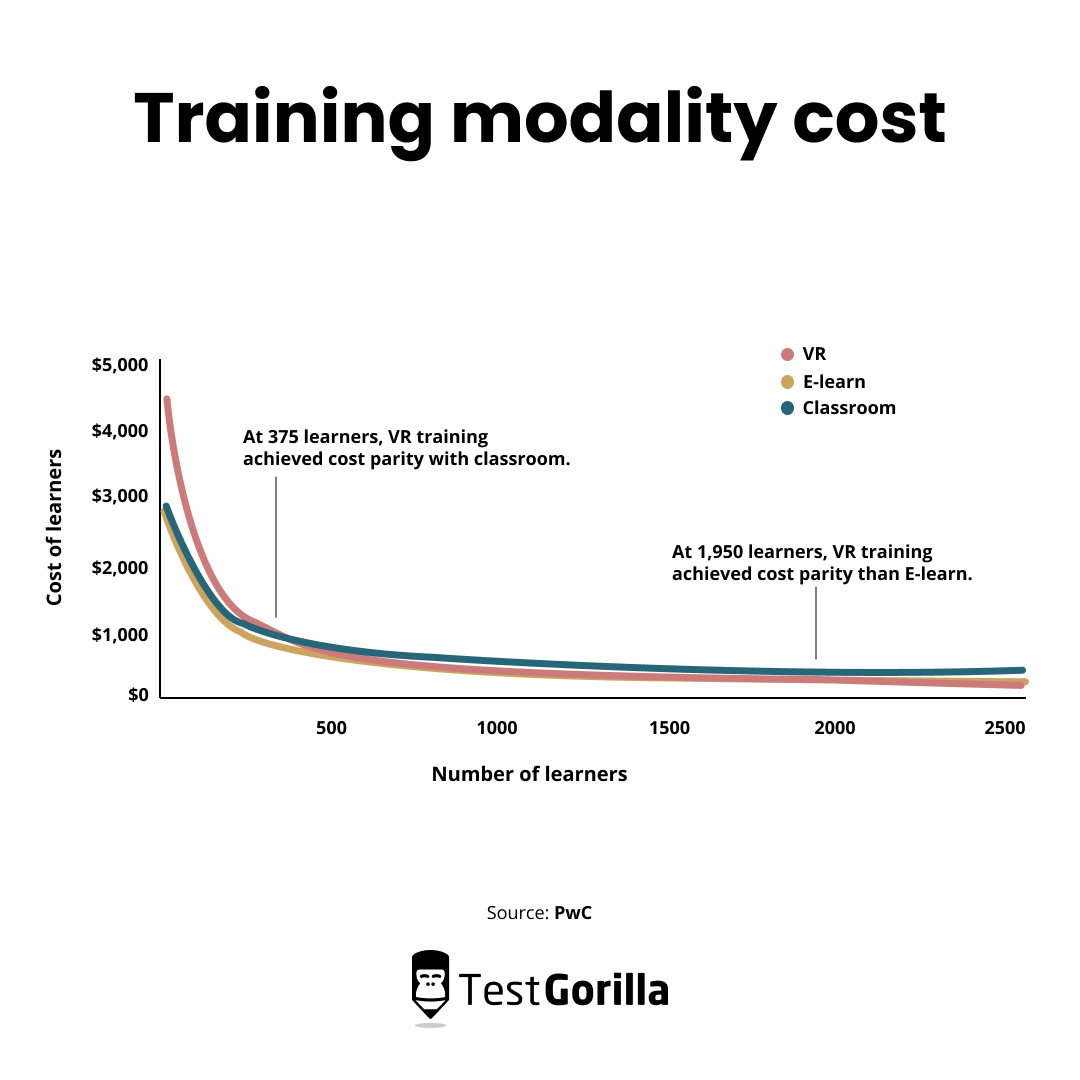
Virtual reality training in the workplace is highly cost-effective when delivered at scale.
PWC’s research further states that the more people companies induct into VR learning, the more money they save on training outright.
It advises that a company would need to train 3,000 learners for VR to be more cost-effective than classroom learning.
However, the research suggests that cost savings increase the more people you induct via VR because training time is reduced significantly.
Here’s how PWC represents the training modality cost for each learner across VR, e-learning, and classroom models:
The cost of VR training in the workplace is higher initially, but the curve flattens as the number of learners increases.
There are hypothetical cost savings through employee retention too, which could help offset the initial cost of VR investment.
For instance, VR learners with more confidence heading into work than classroom learners are less likely to drop out due to frustration or simply not enjoying the job.
Using data from VR training to refine candidate profiles and to create job simulations, Indiana's Child Services Department reduced employee turnover by 31%. It saved money otherwise spent replacing staff, meaning VR paid for itself.[6]
4. Cuts down training and ramp time
Along with other time-saving technology trends like HR automation, VR lessons make training and onboarding more efficient.
Drawing on PWC’s research, VR learners complete training modules four times faster than those learning via the classroom and 1.5 times faster than e-learning trainees.
Specialized research into virtual training for healthcare finds that trainee surgeons are 29% faster at learning skills and are six times as accurate when starting work for real.[7]
VR learning removes new employees’ need to learn on the job. For example, a construction worker could learn how to safely operate a buzz saw through multiple VR training sessions rather than wasting time and effort in the real world.
Cutting ramp time means businesses expect their employees to work more autonomously and produce better quality work more efficiently.
Moreover, staff feel more confident when they head to real work because they have clearer expectations of using skills in practice.
5. Boosts learning retention
The historical Ebbinghaus Memory Experiment proposed that people tend to forget up to 79% of what they’ve learned a month prior. This is known as the “forgetting curve.”[8]
VR training experiences help employees retain the knowledge they learn for longer. Research suggests that 70% of VR trainees remember precise sequences of safety procedures within a week, compared to 20% using traditional training materials.[9]
The forgetting curve model suggests the more relatable the material is, the easier it is to learn. VR environments are relatable and engaging because they emulate real life.
And VR learning surpasses e-learning for knowledge retention. The University of Maryland found that 40% of VR learners scored a minimum of 10% higher on knowledge retention tests than e-learners.[10]
The top industries using VR to train employees
VR training is useful in various industries, whether to help employees stay safe, build confidence, or combine the two.
Here are eight industries that regularly use VR training, with some example use cases.
Industry | Virtual reality training examples |
1. Finance | - Money handling - Customer service, like discussing loans - Addressing potential fraud with customers - Crisis preparation, e.g., bank threats, market crashes, cyberattacks - Application of soft skills after testing |
2. Healthcare | - Surgery practice - Patient outreach, such as discussing sensitive health information or delivering bad news - Crisis preparation, responding to accidents, and providing emergency care - Application of soft skills after testing |
3. Logistics | - Machinery operation - Vehicle handling - Warehouse navigation - Health and safety practice, e.g., lifting and carrying items |
4. Construction | - Tool operation - Working at height and in hazardous situations - Health and safety practice – shielding the public and team members, appropriate tool use - Working with others in dangerous situations |
5. Emergency services | - CPR - Critical thinking in the event of a threat to life - First aid practice - Application of soft skills after testing, e.g., reassuring people and organizing a team |
6. Automotive | - Parts assembly - Vehicle diagnosis and repair - Health and safety practice, such as appropriate use of machinery and working with others - Parts testing, e.g., engines, moving parts |
7. Aviation | - Mock flight training - Emergency response, like during mid-flight - Application of soft skills after testing, including reassuring passengers and critical decision-making in bad weather - Dashboard checks and measures |
8. Defense | - Combat techniques - Fitness training - Use of weaponry and heavy vehicles - Hostile environment handling - Application of soft skills after testing, e.g., hostage or assailant negotiation and critical thinking in risk-to-life scenarios |
5 best virtual reality training tools
Although VR training is still a developing industry, several branded tools are worth researching and investing in for your HR needs.
We’ve reviewed five tools below to help stoke some inspiration.
Factors we considered
When researching tools to include in our breakdown, we took into consideration six major elements:
Ease of scalability: Can companies scale their packages easily and quickly?
Flexibility: How flexible is the tool with different industry demands?
Pricing: Are there flexible options to suit your quarterly budgets?
Ease of use: How steep is the learning curve? And is customization available?
Reputation: How reputable is the end product with users?
Capability: Can the tool manage complex tasks and different learning situations?
Top virtual reality training programs and tools
Tool | How it helps |
STRIVR | Offers a full VR production studio for enterprises to create and manage bespoke scenarios alongside off-shelf products |
Motive.io | Provides storyboard-style VR scenario editing that scales with training needs |
Pixo | Enables trainers to create mixed reality exercises either off-shelf or from scratch, notable for its simple integration with third-party products |
Vrowl.io | Takes care of VR learning development offsite, deploying Metaverse scenarios across three interactivity levels |
UltraLeap | Offers advanced, customizable user tracking for more in-depth and realistic scenarios |
1. STRIVR: Best for larger company needs
STRIVR is a virtual world provider offering simulations with enterprises in mind.
The platform offers an intuitive production studio that trains developers to create real-world simulations. There are levels of complexity and flexibility available, such as off-shelf templates and complete customization.
The platform provides real-time feedback, helping trainers and trainees to adapt and develop mid-scenario, not only at the end.
Pros | Cons |
- Real-time feedback available - Off-shelf VR templates for ease of use - Highly recommended by successful enterprises - Extremely immersive training scenarios - In-depth analytics | - Pricing on request - Can require specialized equipment |
Pricing as of December 2023: Quoted on request.
2. Motive.io: Best for scaling
Motive.io appeals to VR beginners with scalable software that requires zero coding knowledge.
The platform integrates with Unity software, through which users easily create custom models and objects for users to interact with. Training developers put it all together with Storyflow, the brand's authoring tool that scales with individual needs.
The platform provides opportunities for “multiplayer experiences,” meaning you can train several people at once in the same scenario.
Pros | Cons |
- Highly intuitive flow system - Ability to train multiple people at once - No coding required - Enterprise-ready - Real-time data analytics available | - Pricing is only available on request |
Pricing as of December 2023: Quoted on request.
3. Pixo: Best for XR needs
Although Pixo is a market leader for virtual reality outright, its training products extend to XR, meaning you can bring digital assets into the real world to complement training as and when you desire.
This platform is notable for its user-friendly interface, enabling users to easily create and manage modules, assign learners, and track analytics from one device.
The software integrates easily with learning management, meaning you can run it with e-learning and skills initiatives elsewhere.
Pros | Cons |
- Feature-rich - User-friendly HR dashboard - One of the market leaders - Off-shelf content available - Knowledgeable partner that regularly publishes whitepapers and research | - Not many reviews available online - No pricing outwardly available |
Pricing as of December 2023: Quoted on request.
4. Vrowl.io: Best for outsourcing
Vrowl sets itself apart from some of the picks in this list because it offers VR and AR app development beyond training alone. Companies partner with the brand to produce apps and additional in-house experiences.
The provider is an expert in Metaverse deployment and specializes in safety training for various industries. It offers three levels of interactivity: passive, semi-interactive, and fully interactive. It's one of the most flexible platforms on the market.
The service is managed in-house across five core departments, meaning its experts build your AI training completely on your behalf.
Pros | Cons |
- In-house development - Lots of development opportunities beyond training design - Works with a variety of successful brands - Flexible packages are available depending on the interactivity you need - Highly experienced specialists on board | - It might not be the best option if you like to take full control |
Pricing as of December 2023: Quoted on request.
5. UltraLeap: Best for immersion
UltraLeap's biggest selling point is its advanced hand tracking, which helps users interact more easily with the virtual environments you create. Its software is adaptable to multiple industries, with aircrew, healthcare, and corporate applications suggested by the brand.
The manufacturer operates via Gemini technology, which is highly adaptable to different hardware and applications. It integrates smoothly with Unreal and Unity for 3D object development and deployment.
The manufacturer provides users with motion controllers, hand tracking, and extensive tracking that’s easy to integrate.
Pros | Cons |
- Impressive hardware standards - Customizable for various needs - Highly flexible around developers and third-party objects - Lots of documentation and advice available - Highly immersive and interactive experience | - No pricing available |
Pricing as of December 2023: Quoted on request.
6 best practices for leveraging VR training in your HR department
After choosing the ideal training tool for your needs, it’s time to learn about six best practices to make the most of your new tech.
Best ways to harness the power of VR training technology
Best practice | Brief summary |
1. Clarify your VR training goals | Look for skill and learning gaps in your training setup, ask employees for feedback, and lay out long-term goals so you can get the best value from VR training |
2. Be mindful of virtual fatigue | Create short VR sessions to prevent fatigue and illness, and make your workers aware of the risks |
3. Educate people on VR | Show people how to use hardware safely and effectively with guides and learning modules based on your manufacturer’s recommendations |
4. Use talent assessments to personalize VR training | Skills test your employees to find knowledge gaps you can prioritize when designing lessons with a VR provider |
5. Use VR to boost soft skills and implement diversity training | Build scenarios where staff can practice social challenges to build confidence without risking reputational damage |
6. Monitor VR analytics and leverage metrics | Track completion rates and interactivity data to refine your scenarios to fit employees better in the future |
1. Clarify your VR training goals
Always plan out what you'd like to achieve through VR before using new tools. This way, you spend less time on trial and error.
Start by thinking of any potentially dangerous or costly scenarios in your business.
If you work in automotive, you might need to replicate the car-building process to avoid wasting materials. In construction, you could build a VR scenario to help trainees get up to speed with power tools and working high up.
Remember, building a fully operational VR environment with an off-site developer can take two months or more.[11]
Consider your existing training practices and map out the stages your trainees go through. When working with your employees, make a note of:
Different learning styles among your staff
Areas where people lack confidence
Potential safety concerns that VR could help support
Which employees, and how many, are interested in VR as a training option
Training outcome data, e.g., how long it takes trainees to get up to speed
Technical skill gaps with specific tools, equipment, and software
Then, consider your long-term VR goals to help define your analytics practice in the future. For example, adopt VR training solutions to:
Reduce employee accidents
Improve staff confidence and boost retention
Make training more efficient
Share your goals with your chosen developer to ensure the end scenarios are on point.
2. Be mindful of virtual fatigue
Although everyone experiences VR differently, taking breaks from headsets every 20 to 30 minutes is healthy.
VR fatigue sometimes causes dizziness, nausea, disorientation, loss of spatial awareness, and seizures in rare cases. Most VR hardware manufacturers advise taking breaks of at least 15 minutes for every 20 to 30 minutes of use.
Market leader Oculus advises that one in 4,000 people might experience seizures or blackouts through unhealthy exposure to virtual reality.[12]
Prioritize employee wellness and run risk assessments before you deploy VR for training employees. Do any workers experience blackouts or seasickness, or does anyone have epilepsy?
Then, closely monitor how much your employees use VR and ensure they work within healthy limits.
Once staff know the risks and have experience using the hardware, consider carefully setting up VR for employee self-service training to save time and effort.
3. Educate people on VR
Once you've gotten a grip on VR and its benefits, you must carefully introduce it to your employees and set up usage training sessions.
Remember, not everyone feels comfortable using VR, and some people can't use it because of a medical condition. Always provide separate learning routes.
For those who are receptive but unsure what to expect, show your employees:
Why you’re implementing VR training
The outcomes you intend to achieve
Positive impacts it could have on their development
Plan time aside to let people learn to properly fit the hardware. Also, prepare a room with plenty of space and introduce them to the training manual.
You could repurpose elements of the training documents and safety information provided for the VR kit into e-learning modules, such as through an employee wellness platform.
VR experts advise that an initial hour of training is likely enough to cover core aspects of how to use the tech. However, additional exercises in bursts of 15-30 minutes are likely enough to get people up to speed.[13]
4. Use talent assessments to personalize VR training
Before designing a VR scenario, assess your employees for the skills they need for their roles.
You could create a set assessment plan with talent assessment software based on a specific role that covers core competencies and power skills.
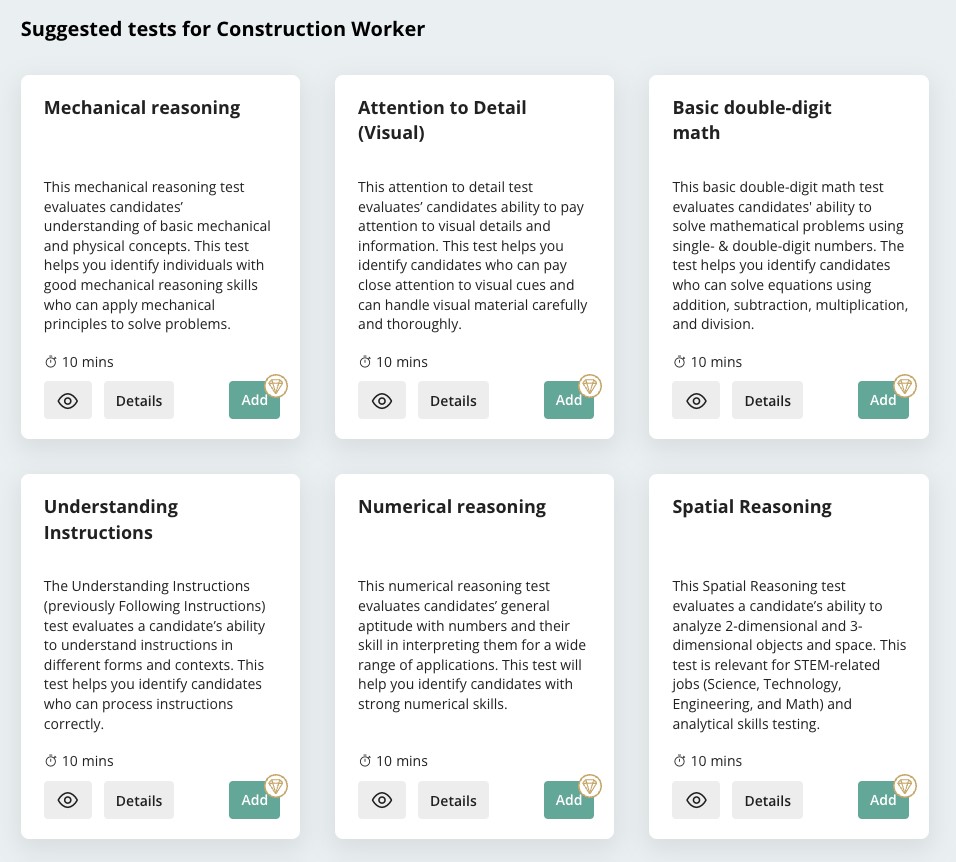
Let’s say you’re training a construction worker – here are some automated assessments TestGorilla recommends:
When analyzing the skills test data, look for areas employees lack knowledge and prioritize these for VR training.
And remember that your skill needs could change in the future. For instance, you might need to refocus on niche skills.
Therefore, create multiple assessment plans to account for future needs and ensure your development team offers scalability.
5. Use VR to boost soft skills and implement diversity training
Soft skills, or power skills, are highly desirable but often difficult to teach.
Collaboration, problem-solving, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence skills, for example, demand social interaction and physical practice.
Poor power skills are common among bad hires, according to 89% of hiring managers. You should always test potential hires for these skills during recruitment because it's just as important to prioritize practicing them in training.[14]
Through VR, you could create a social problem for a trainee to solve, such as handling a customer query.
Observe their problem-solving skills in motion, then give feedback about how they performed and let them try again.
You could even use VR software that allows multiple users to practice collaborating in a mock scenario and monitor their teamwork skills.
VR training also helps you create scenarios that build diversity awareness. For example, you could create a mock situation where your team has to provide customer care to people of different races or cultures.
Alternatively, have them “sit in” on potentially charged mock scenarios where they learn to pick up on body language and bias.
6. Monitor VR analytics and leverage metrics
Use VR tools with dashboards to track how long trainees take to complete your scenarios and how many attempts each employee takes to complete puzzles.
These metrics could show they need support with an area of the program, which can then be discussed during one-on-one meetings.
Then consider using built-in HR analytics software to track how effective your VR program is. By monitoring training in real-time, you can see whether or not the challenges you set are too complex.
Training scenarios where you encourage employees to take different routes based on emotional responses could help inform you of their personalities and how they solve problems.
Combine the data from these metrics with personality tests to learn more about how employees work with others.
You can also use data from VR analytics with performance management systems to track how recruits develop over time, too.
Finally, VR and people analytics customized for each user help you tailor personal development sessions to employees' long-term needs.
For example, if you find one employee who shows good management skills in VR scenarios, consider prioritizing them for a leadership development plan.
3 examples of companies succeeding with VR training
Training in VR is growing popular with many firms, but the following three companies are leading the way for VR training adoption:
Walmart
Volkswagen
Hilton
Let’s take a look at why.
Walmart
Walmart, the US superstore, uses an immersive learning program to place recruits in the heart of customer care before they set foot in a physical location.
The brand partnered with VR experts to reduce business disruption and produce repetitive, safe, and memorable experiences for new hires.
Beginning with a pilot, the company expanded its in-store VR scenarios to thousands of units nationwide on the back of a 15% boost in knowledge retention and an increase of 30% in employee satisfaction.
Programs offered by the firm include "Holiday Rush" mode, where recruits learn how to handle high-traffic periods for the store, providing integrated features like register training.[15]
Volkswagen
Volkswagen, the automotive giant, takes away the risk of mistakes in employees' first few weeks on the assembly line by providing a full VR experience of installing and building vehicles at a realistic pace.
The firm’s VR scenario sees trainees completing specific assembly tasks – such as installing brakes effectively – to be more productive and efficient when heading to the assembly line.
So far, more than 10,000 staff in the company have received VR training across more than 30 different modules. The system saves the company money and provides much-needed confidence to staff and management.[17]
Hilton
Hilton uses VR to help corporate teams understand how its hospitality business works in practice.
By providing realistic hotel scenarios for corporate training, employees who typically work outside of hotels gain empathy for staff and understand daily operations better.
VR tech has also helped the brand reduce in-class training from four hours to 20 minutes per person. The company’s environments help trainees practice customer interactions without the risk of upsetting a customer or making a costly error.[17]
Embrace VR training and inspire more capable, confident employees
VR training might seem like a scary new technology in some ways, but it’s no longer a distant concept – and it’s far more helpful than scary.
What’s more, VR isn’t just a trend in recruitment tech that will disappear as quickly as it emerged; companies worldwide are investing, and realistic VR training scenarios are set to become common practice within a few years.
Using VR technology, you can:
Help employees realize their skill potential
Boost learning and development efficiency
Fill skill gaps and find new opportunities
Reduce training costs at scale
If you've found our deep dive into VR employee training insightful, we recommend learning about gamification in HR through our complete guide.
From there, take a closer look at how to introduce AI in HR to your tech stack for an even sleeker, more efficient skills-based workforce.
When you're ready to start testing skills to complement your VR modules, head to the TestGorilla library for inspiration.
VR Training FAQs
To close, let’s break down some common questions about virtual reality training.
What are the disadvantages of VR training?
Used inappropriately, VR training can cause dizziness and nausea after too long. Upfront costs for VR equipment used in training are typically more expensive than classroom and e-learning, and some users might feel they struggle with traditional training if they become too dependent on VR.
Learn more about combating VR fatigue in our guide.
Is virtual reality training expensive?
VR training is more expensive than traditional education initially. It's an investment of thousands of dollars in hardware and setting up partnerships with developers. However, at scale, this type of program is cost-effective.
Is VR training better than traditional training?
Research shows VR training helps trainees engage more with educational material, gain more confidence, and learn techniques faster than through traditional means. However, some learners prefer to study through classrooms and e-learning modules.
Sources
1. “What does virtual reality and the metaverse mean for training?”. (September 15, 2022). PWC. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://www.pwc.com/us/en/tech-effect/emerging-tech/virtual-reality-study.html
2. Barnard, Dom. (June 14, 2023). “History of VR - Timeline of Events and Tech Development”. VirtualSpeech. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://virtualspeech.com/blog/history-of-vr
3. Boris, Vanessa. (December 20, 2017). “What Makes Storytelling So Effective For Learning?”. Harvard Business Publishing. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://www.harvardbusiness.org/what-makes-storytelling-so-effective-for-learning
4. “Virtual Reality in Education Market Size, Share & COVID-19 Impact Analysis, By Component (Hardware, Software, and Content), By Application (K-12, Higher Education, and Vocational Training), and Regional Forecast, 2023– 2030”. (2023). Fortune Business Insights. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/virtual-reality-in-education-market-101696
5. “Data Breach Investigations Report 2022”. (2022). Verizon. Retrieved November 25, 2023. https://www.verizon.com/business/resources/T1bb/reports/dbir/2022-data-breach-investigations-report-dbir.pdf
6. Stackpole, Beth. (October 15, 2020). “How virtual reality can help improve employee retention”. MIT Management: Sloan School. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/how-virtual-reality-can-help-improve-employee-retention
7. Seymour, Neal E., et al. (October 2002). “Virtual Reality Training Improves Operating Room Performance”. Annals of Surgery. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1422600/
8. “How Fast Do Students Forget And How Can VR Help?”. XpertVR. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://xpertvr.ca/how-fast-do-students-forget-and-how-can-vr-help/
9. Sankaranarayanan, Ganesh, et al. (August 2018). “Immersive virtual reality-based training improves response in a simulated operating room fire scenario”. Surgical Endoscopy. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322705389_Immersive_virtual_reality-based_training_improves_response_in_a_simulated_operating_room_fire_scenario
10. Krokos, Eric; Plaisant, Catherine; Varshney, Amitabh. (16 May, 2018). “Virtual memory palaces: immersion aids recall”. Virtual Reality. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10055-018-0346-3
11. “How Long Does It Take To Develop VR Training Content?”. Roundtable Learning. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://roundtablelearning.com/how-long-to-develop-vr-training-content/
12. “Oculus Rift and Touch Warnings”. Oculus. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://securecdn.oculus.com/sr/oculusrift-warning-english (PDF download)
13. Barnard, Dom. (January 18, 2023). “Guide for training employees in VR (from 1000s of hours of experience)”. VirtualSpeech. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://virtualspeech.com/blog/guide-training-employees-vr
14. “2019 Global Talent Trends”. (January 2019). LinkedIn Talent Solutions. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://business.linkedin.com/content/dam/me/business/en-us/talent-solutions/resources/pdfs/global_talent_trends_2019_emea.pdf
15. “In the footsteps of trailblazers: How Walmart embraces Immersive Learning”. STRIVR. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://www.strivr.com/customers/walmart/
16. “Volkswagen | Assembly VR Training”. (May 25, 2021). Vrowl. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://www.vrowl.io/volkswagen-assembly-vr-training/
17. “Hilton Case Study: Building empathy to enhance hospitality”. Oculus for Business. Retrieved November 24, 2023. https://business.oculus.com/case-studies/hilton/
You've scrolled this far
Why not try TestGorilla for free, and see what happens when you put skills first.